rSIM vs. The Rest: Ensuring “Always-On” Connectivity.
In today’s world, reliable mobile connectivity is no longer a luxury; it’s a critical lifeline for businesses and individuals alike. From remote patient monitoring in telecare to payment terminals and Micro-mobility scooters, countless applications depend on uninterrupted data flow. Unfortunately, network outages are a persistent reality, leading to disruptions, lost productivity, and even safety risks.
This is where innovative technology like rSIM come into play. rSIM stands for “Resilient SIM,” and it lives up to its name by ensuring “Always On” cellular connectivity for your IoT devices. But how does rSIM differ from other SIM technologies like multi-IMSI SIMs, eSIMs, and traditional roaming SIMs? Let’s delve deeper and understand what makes rSIM the champion of reliable connectivity.
What is rSIM?
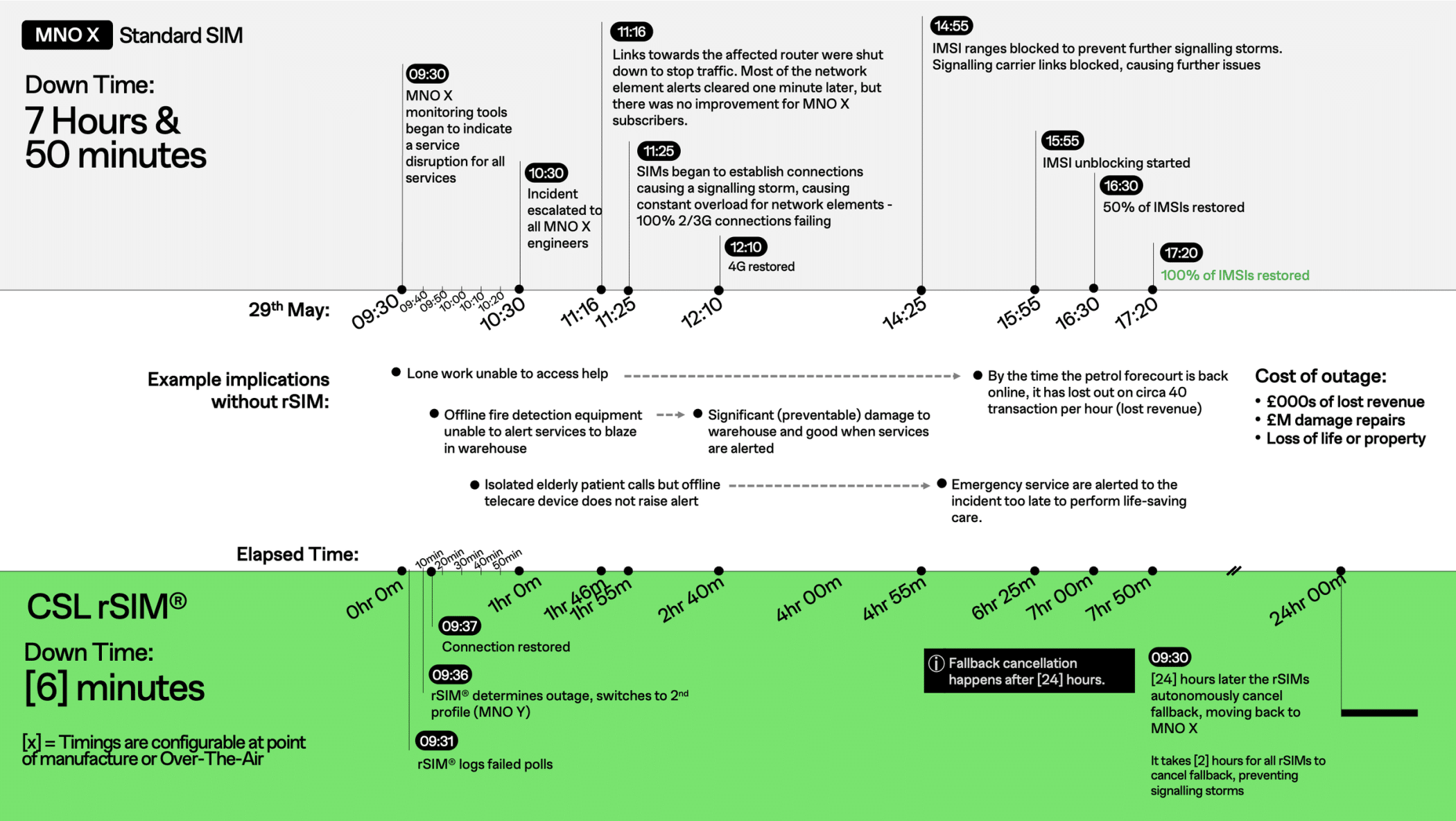
rSIM is a unique SIM card designed to provide automatic failover to a backup network in case of an outage on the primary network. Think of it as a safety net for your cellular connection. The rSIM continuously monitors network performance and, if it detects an issue, it allows the device to attempt roaming across available networks. If the device cannot establish a connection, the rSIM will then autonomously switch to a secondary network profile stored on the SIM card. This proactive approach ensures your devices stay connected, even during network disruptions.
Each of the two network profiles stored on the SIM card contains its own IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity), and these IMSIs are linked to entirely separate mobile operator cores, with no shared infrastructure. This “Dual Core” approach significantly reduces the likelihood of losing connectivity, as it’s extremely rare for two independent mobile operators to experience outages at the same time.
rSIM vs. Multi-IMSI SIM: Don’t Be Fooled by Lookalikes.
At first glance, multi-IMSI SIMs might seem similar to rSIMs. Both offer multiple network profiles on a single SIM card. However, there are some crucial differences:
-
Network Monitoring and Failover: Here’s where rSIM truly shines. It actively monitors network performance and triggers an automatic switch to the backup network if an outage occurs. Multi-IMSI SIMs often lack this proactive functionality and may not detect network issues, leaving your device disconnected.
-
Dual Core: Multi-IMSIs are normally provided by MVNOs (Mobile Virtual Network Operators)and they link the multiple-IMSIs to their single core. If that core goes down, all the IMSIs will stop working. rSIM uses diverse mobile operator cores. This diverse Dual-Core approach means rSIM will always stay connected.
-
Standards Compliance: rSIM is a fully GSMA-compliant SIM card, ensuring compatibility across a wide range of devices. Multi-IMSI solutions, on the other hand, often lack standardised protocols, potentially leading to compatibility issues with certain devices.
-
Device Agnostic: A key advantage of rSIM is that it is device agnostic, meaning it works seamlessly with any device that supports a standard SIM card. In contrast, Multi-IMSI solutions often require specific configurations or inputs from the device—requirements that may not always be supported by all devices. As a result, these solutions may face compatibility issues across different devices.
-
Resilience vs. Cost Focus: While Multi-IMSI solutions sometimes aim to optimise costs by steering devices towards cheaper networks, rSIM prioritises maintaining a stable connection regardless of cost. This is crucial for applications where downtime can have severe consequences.
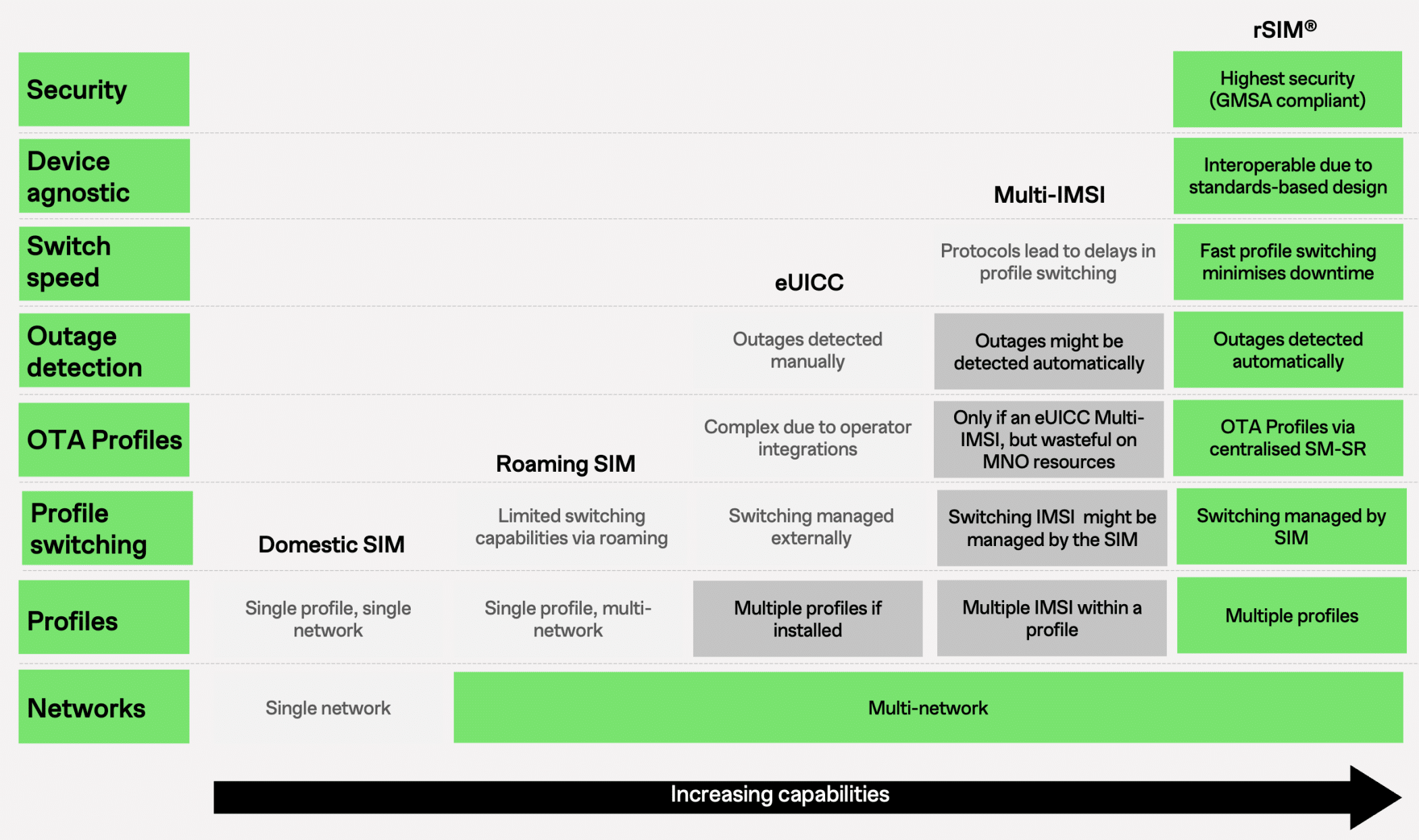
rSIM vs. eSIM: Partners, Not Rivals.
At its core, rSIM is an advanced form of eSIM, offering all the benefits of embedded SIM technology but with enhanced resilience. Some may wonder if eSIM (embedded SIM) technology conflicts with rSIM, but in reality, they are inherently the same. rSIM builds upon eSIM’s foundation, incorporating its advantages like remote profile management and smaller size while adding the critical feature of autonomous network resilience. While a standard eSIM allows users to download and switch profiles remotely, rSIM takes this further by autonomously testing network connections and switching between operator cores in real-time when disruptions are detected.
By combining eSIM’s flexibility with rSIM’s automatic failover capabilities, users achieve a future-proof solution that not only leverages the benefits of remote management but also ensures uninterrupted connectivity through its intelligent, self-sufficient switching mechanism.
rSIM vs. Roaming SIM: Beyond Basic Roaming.
Roaming SIMs allows users to stay connected when travelling outside their home network. While this is useful for international travel, roaming SIMs have limitations:
-
Core Network Reliance: A roaming SIM relies on the core network of the roaming provider. If that core network experiences an outage, the device loses connectivity entirely, even if other networks are available.
-
Limited Resilience: Roaming SIMs offer basic roaming functionality but lack the proactive failover capabilities of rSIM.
-
Permanent Roaming: Restrictions on permanent roaming are increasing, making the deployment of roaming SIMs in certain countries impossible. rSIM addresses this challenge by utilising a combination of profiles from both local and international providers. This ensures compliance with local regulations while maintaining the flexibility of roaming across multiple networks.
Imagine a medical professional using a device with a roaming SIM to monitor a patient’s vitals remotely. If the roaming provider’s core network goes down, the critical connection to the patient is lost, potentially jeopardising their health. rSIM, on the other hand, would detect the outage and switch to a backup network, ensuring uninterrupted monitoring.
The Following example shows how an 8-hour outage on a normal SIM vs rSIM and the consequences of being disconnected:
When to Choose rSIM: Prioritising “Always-On” Connectivity
So, when does it make sense to use rSIM? Consider rSIM for any application where uninterrupted connectivity is critical, and where a loss of service could cause significant problems. Examples include:
-
Healthcare: In remote patient monitoring, a failure in connectivity can mean delayed responses in life-critical situations. Ambulances rely on real-time data transmission to communicate with hospitals—any network disruption can lead to dangerous delays.
-
Security Systems: rSIM is vital for alarm monitoring and remote access control. In high-security environments, any connectivity outage can leave properties vulnerable to unauthorised access or result in unmonitored alarms during break-ins.
-
Industrial Automation: For machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, especially in monitoring critical infrastructure, network downtime could halt operations or lead to inaccurate reporting, causing costly delays in manufacturing or utilities management.
-
Transportation and Logistics: In fleet management, micro-mobility solutions such as rentable scooters depend on constant connectivity to ensure users can find, unlock, and pay for their rides. Disruptions in service can result in lost revenue and poor user experience. Similarly, in tracking high-value goods, uninterrupted data transmission ensures goods are monitored for safety and timely delivery.
-
Payment Systems: Whether it’s for point-of-sale machines in retail or mobile payment kiosks, such as those used in micro-mobility stations, losing connectivity means losing transactions. This directly impacts revenue, especially in fast-paced environments where customers expect seamless, real-time payments.
-
Utilities: Monitoring and control systems for power grids or water treatment plants require consistent communication to operate effectively. A lapse in connectivity can cause system failures, service interruptions, or even public safety risks.
While the initial cost of rSIM might be slightly higher than traditional SIM cards, the benefits of uninterrupted connectivity often outweigh the additional investment. Consider the potential financial losses due to downtime. The rSIM white paper dives deeper into the growing need for resilient connectivity and the impact of network outages on businesses.
The Cost of Downtime: Why rSIM Makes Financial Sense
While rSIM may be slightly more expensive compared to traditional SIM cards, the cost of downtime can be far greater. The rSIM white paper, titled “The High Cost of Downtime: How Businesses Can Ensure Uninterrupted Connectivity” explores this topic in detail. Here are some key findings from the white paper:
-
97% of businesses experience some form of connectivity loss every month.
-
Nearly two-thirds (63%) of businesses have lost sales or customers due to connectivity issues.
-
Connectivity failures have caused frustration in 83% of businesses and even violence in 40%.
These statistics paint a clear picture: downtime is not just an inconvenience; it can have a significant financial and operational impact. By ensuring “always-on” connectivity, rSIM helps businesses avoid these costly disruptions.
Learn More About rSIM and the Future of Reliable Connectivity
If you’re looking for a solution to guarantee uninterrupted cellular connectivity for your critical devices, look no further than rSIM. Its unique combination of autonomous failover, device agnosticism, and GSMA compliance makes it the most reliable SIM solution on the market.
Download the rSIM white paper, to learn more about the growing need for resilient connectivity and how rSIM can help your business thrive in the face of network challenges: